Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199
Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199

Grade 310/310S is an austenitic stainless steel, which offers exceptional high temperature properties, along with good ductility and weldability.
Austenitic stainless steel alloy 316 / 316L is a molybdenum-bearing grade. The high nickel and molybdenum content in these pipes offer better overall corrosion resistant properties compared to 304 grade SS. This resistance is particularly useful regarding pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride environments. Moreover, 316 / 316L stainless steel tubes and pipes demonstrate exceptional high temperature tensile, creep, and stress-rupture strengths. Formability and weldability is also excellent. Unlike grade 316, 316L pipes are immune from sensitization, due to lower carbon content. Thus, it is commonly used in heavy gauge welded components.
316 Stainless Steel Tube is a popular material used in many industrial and commercial applications due to its high corrosion resistance, strength, and other advantageous properties. Its unique chemical composition plays a vital role in achieving these characteristics. Consisting mainly of iron, it also contains chromium, nickel, manganese, silicon, carbon, and small amounts of nitrogen and molybdenum. Chromium significantly increases corrosion resistance by forming an invisible passivation film on the surface of the steel that helps inhibit oxidation. Adding nickel further enhances this property, as does the molybdenum, which strengthens the overall structure by preventing sulfur from reacting with these elements. Altogether, 316 stainless steel tube provides superior performance in harsh conditions making it both cost-effective and reliable over time.
SS 316 Tube offers an array of advantageous properties and different uses in various industries. Its level of corrosion resistance is higher than other alloys, making it an ideal choice for projects exposed to harsh environments or excessive temperatures. The bright steel finish also makes it attractive for external applications. Due to its excellent machinability, this material is frequently utilized in food processing and chemical industries where easy assembly and sterile conditions are paramount. 316 Stainless Steel Tube has a high tensile strength that allows for the fabrication of solid components with thinner walls, allowing for lighter weight and enhanced cost-efficiency. This material also offers outstanding weldability, further contributing to its versatility across many sectors.
316l stainless steel tubing consists of remarkable chemical composition that makes it more resistant to corrosion and tarnishes. It is an austenitic stainless steel containing molybdenum, increasing its resistance to chloride-rich environments and other corrosive media. It also has a higher carbon content than standard 316 stainless steel tubing, making it withstand high temperatures up to 1700 degrees F without any negative impact on the material’s strength or durability. This grade of tubing also contains low levels of phosphorus and sulfur, which helps resist stress-corrosion cracking during service in highly saline fluids. Overall, 316l stainless steel tubing offers excellent performance for applications requiring increased strength and corrosion resistance.
316L SS tubing is an excellent choice for piping applications due to its impressive combination of properties. Its corrosion-resistant nature and resistance against extreme temperatures make it ideal for high-pressure, steam-laden environments. In addition, this type of tubing has superior wear resistance and a very good tolerance for forming and welding. These properties create the potential for its use in many industries, such as commercial food processing plants, chemical refinery systems, and marine and aerospace applications. Not only is it cost-effective compared to other steel alloys, but its remarkable strength also makes it perfect for various medical instruments, particularly when hygiene is a priority. Therefore, our 316L stainless steel tubing suppliers offer desirable custom types and shapes with exceptionally reliable performance.
The following sections describe the properties of 316 / 316L stainless grade pipes supplied by Arch City Steel & Alloy:
Better resistant in many atmospheric environments and various corrosive media compared to grade 304.
Resistant to stress corrosion cracking above about 122°F (50°C).
Good resistant to pitting and crevice corrosion in warm chloride environments.
Corrosion resistance to potable water at ambient temperature range is up to 1000mg/L of chlorides. This reduces to about 500mg/L at 140°F.
316 / 316L is commonly known as “marine grade stainless steel”, although it is not resistant to warm sea water.
Exceptional oxidation resistance in continuous service to 1700°F (925°C) and in intermittent service to 1600°F (870°C)
Typical Chemical Composition % (max values, unless noted)
| Grade | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | N |
| 316 | 0.08 max |
2.0 max |
0.75 max |
0.045 max |
0.03 max |
min: 16.0 max: 18.0 |
min: 2.0 max: 3.0 |
min: 10.0 max: 14.0 |
0.10 max |
| 316L | 0.03 max |
2.0 max |
0.75 max |
0.045 max |
0.03 max |
min: 16.0 max: 18.0 |
min: 2.0 max: 3.0 |
min: 10.0 max: 14.0 |
0.10 max |
Typical Room Temperature Mechanical Properties
| Grade | Tensile Strength KSI (min.) |
Yield Strength 0.2% Offset KSI (min.) | Elongation % in 2ʺ(50.8 mm) | Hardness (Brinell) MAX |
Hardness (Rockwell B) MAX |
| 316 | 75 | 30 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
| 316L | 70 | 25 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
Custom Grades of Stainless Steel Tube
316 grade stainless steel tubes are robust, easy to maintain, and formable. These advantages result from alloying the base austenitic steel with other elements.
316 stainless steel alloys are often more expensive because they use rare elements to alloy them and are therefore not widely available. But they do provide better performance in certain areas, such as corrosion resistance and strength. That makes 316 the preferred choice for many applications.
Stainless steel is an ideal corrosion-resistant material, but only if made correctly. 316 grade stainless steel tube is economical and suitable for most environments but lacks the 316’s chloride resistance. Although slightly more expensive, 316 is worth the extra money in areas of high exposure to chlorides. Depending on the purpose, different grades are best for different applications. Some standard consumer stainless steels include 430, 409, and 316.
Strength
The austenitic structure of 316 stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance. Compared to 304, this stainless steel is much more resistant to pitting and crevice corrosion. This stainless steel still maintains its excellent toughness despite the high chromium content, even at very high temperatures. Hence, it is widely used for cryogenic applications. This type of steel has excellent toughness, weldability, and dimensional stability.
Easy maintenance
The best way to keep your 316 stainless steel tubes in good condition is to avoid cleaning them with sewage or other chemicals. To maintain their luster, scour them twice a year. If your 316 stainless steel pipes are external, they will usually be subject to rain erosion. To prevent dust accumulation, you can combine rain wash with manual cleaning. You can use a cleaning solution of 2% hydrofluoric acid and 10% nitric acid.
Superior corrosion resistance
316 stainless steel tubes are commonly used for a wide variety of applications. This high-quality steel is a member of the austenitic group, comprising two-thirds of all stainless-steel production. The primary alloy composition is 16 to 18 percent chromium, 10 to 14% nickel, and two to three percent molybdenum. Other alloying elements are added for enhanced toughness and corrosion resistance.
Economical
A 316 stainless steel tube provides several benefits compared to standard metal tubing. They are corrosion-resistant, lightweight, easy to clean, and relatively inexpensive. Although their initial cost may be higher than that of other types of tubing, they are typically less expensive to replace and maintain in the long run. Below, we discuss the benefits and applications of 316 stainless steel tubing. This type of tubing can be used in various applications, from kitchenware to corrosive environments.
Resistant to chlorides
Stainless steel grade 316 is more resistant to corrosive agents such as sulfuric acid and other oxidizing acids. Compared to type 304, 316 stainless steel is more resistant to chlorides, bromides, and fatty acids at high temperatures. This makes it a better choice for applications involving strong acids and salt. Despite its high resistance to chlorides, Type 304 is also resistant to most oxidizing acids and other chemicals.
Final Take
Stainless steel is a versatile material, and 316 stainless steel is no exception. The material’s corrosion resistance is excellent, while its ease of workability is second to none. Stainless steel is also solid and valuable for many industrial applications. Stainless steel tubes made of 316 grades are lightweight and easy to work with, ideal for smaller parts. Stainless steel tubes made from 316 grades are one of the most popular grades in the world. Call 1.636.343.3004 for more information.
316 / 316L stainless steel pipes are majorly used for following applications:
Considering the importance of outside and inside surface of stainless steel tubes for fluid power industry, Our mills are providing tubes that are free from scale, rust, seams, laps.
Additional mechanical or physical properties may also need to be considered to achieve the overall service performance requirements.
| Item | ASTM A213/A213M | ASTM A312/A312M | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | TP304 | TP304L | TP304 | TP304L |
| TP316 | TP316L | TP316 | TP316L | |
| TP317 | TP317L | TP317 | TP317L | |
| TP347 | TP310S | TP347 | TP310S | |
| TP309H* | TP310H* | TP317* | TP310H* | |
| TP321HΔ | TP321HΔ | |||
| Grade | C (max) | Si (max) | Mn (max) | P (max) | S (max) | Ni | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP 304 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 8-11 | 18-20 |
| TP 304H | 0.04-0.10 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 8-11 | 18-20 |
| TP 304L | 0.035 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 8-13 | 18-20 |
| TP 309S | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 8-13 | 18-20 |
| TP 310S | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 12-15 | 22-24 |
| TP 316 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 19-22 | 24-26 |
| TP 316L | 0.035 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 10-15 | 16-18 |
| TP 316Ti | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11-14 | 16-18 |
| TP 317 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11-14 | 16-18 |
| TP 321 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9-13 | 18-20 |
| TP 321H | 0.04-0.10 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9-13 | 17-20 |
| TP 347 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9-13 | 17-20 |
| TP 347H | 0.04-0.10 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9-13 | 17-20 |
| Grade | Tensile Strength Min(Mpa) | Yeild Point Min(Mpa) | EL. Min(%) | Rockwell Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP 304 | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 304H | 550 | 240 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 304L | 485 | 170 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 309S | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 310S | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 316 | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 316L | 485 | 170 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 316Ti | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 317 | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 321 | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 321H | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 347 | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
| TP 347H | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 |
Heat treatment technology of stainless steel pipe surface
For the heat treatment technology of the surface of stainless steel pipes, non-oxidation continuous heat treatment furnaces with protective gas are generally used abroad for intermediate heat treatment and final heat treatment of finished products. As a bright surface without oxidation can be obtained, the traditional pickling process is eliminated. The adoption of this heat treatment process not only improves the surface of stainless steel pipes, but also overcomes the environmental pollution caused by pickling.
According to the manufacturer of stainless steel pipes, according to the current world development trend, bright annealing continuous heat treatment furnaces are basically divided into the following two types:
(1) Roller-type bright annealing heat treatment furnace.
This bright annealing furnace type is suitable for heat treatment of large-size and large-volume special-shaped stainless steel pipes, with an hourly output of above 1.0 Tons. The protective gases that can be used are high-purity hydrogen, decomposed ammonia and other protective gases. It can be equipped with a convection cooling system to cool the special-shaped stainless steel tube faster.
(2) Mesh belt type bright annealing heat treatment furnace.
This bright annealing furnace type is suitable for small-diameter thin-walled precision special-shaped stainless steel pipes. The hourly output is about 0.3 to 1.0 Tons. The length of the steel pipe can be up to 40m. It can also be used to process capillary tubes in coils. Equipped with convection cooling system for fast cooling. Using gas fuel or electric heating, various protective gases can be used. The stainless steel pipe after this furnace-type heat treatment has no scratches and good brightness surface.
Tensile test and hardness test of stainless steel pipe?
Tensile strength test is to make a sample of stainless steel pipe, pull the sample to break on a tensile testing machine, and then measure one or several mechanical properties, usually only the tensile strength, yield strength, elongation after fracture and section are measured Shrinkage. Tensile strength test is the most basic test method for mechanical properties of metal materials. Almost all metal materials require tensile test as long as they have requirements for mechanical properties. Especially for those materials whose shape is not convenient for hardness test, tensile strength test becomes the only means of testing mechanical properties.
The hardness test is to slowly press a hard indenter into the surface of the sample with a durometer under specified conditions, and then test the depth or size of the indentation to determine the hardness of the material. Hardness test is the simplest, fastest and easiest method in material mechanical property test. The hardness test is non-destructive, and there is an approximate conversion relationship between the material hardness value and the tensile strength value. The hardness value of the material can be converted into the tensile strength value, which has great practical significance.
Because the tensile strength test is not easy to test, and it is convenient to convert the hardness to the strength, more and more people only test the hardness of the material and less test its strength. In particular, due to the continuous advancement of hardness tester manufacturing technology and innovations, it is now possible to directly test the hardness of some materials that could not be directly tested before, such as stainless steel tube, stainless steel sheet and stainless steel strip. Therefore, there is a tendency for hardness tests to gradually replace tensile tests.
Our specialized process for seamless tubing manufacturing begins with either an extruded hollow tube or a solid bar drilled to our exacting specifications. The material is then reduced in size a number of times through various cold working techniques until it reaches the specific size, tolerances, and temper required by our customer. After each cold working cycle the tubes are cut, cleaned and heat treated in preparation for the next cold working step.
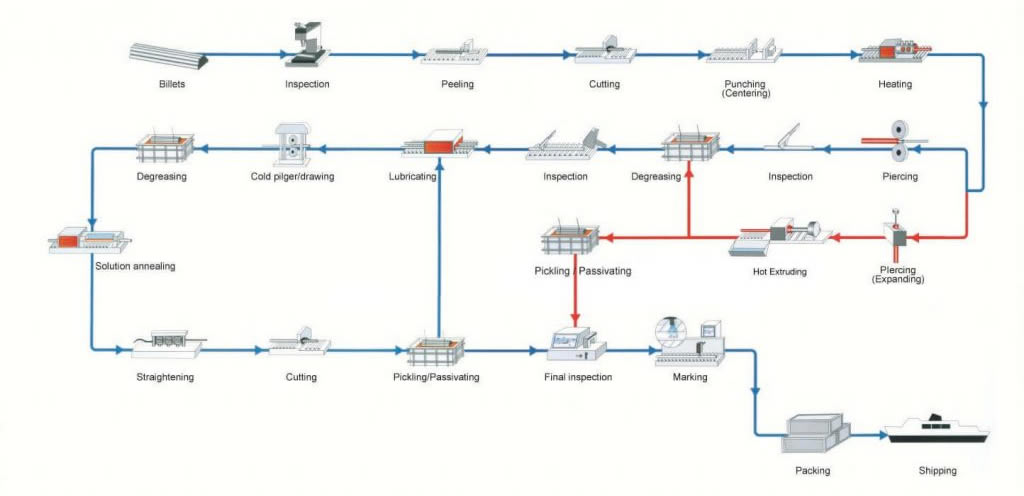
Pilfering
Pilfering reduces the size of the tube across three dimensions – outside diameter (OD), internal diameter (ID) and wall thickness. We roll a die set with a tapered groove across the outside of the tube while supporting the inside diameter using a taper-matched, hardened steel mandrel.
In a single cold working step, we can achieve a significant reduction in cross-sectional area while minimizing material loss and, most importantly, improving the material’s microstructure. Seamless tubes constitute the majority of volume processed by tube reducing or pilgering.
Cold Rolling
Like pilgering, tube rolling also uses compression to reduce the size of seamless tubes. However, while pilgering uses a pair of grooved, tapered dies to work the metal over a tapered mandrel, tube rolling utilizes one or two sets of rolls with constant cross-section grooves on the circumference of the tube.
Generally, the process employs a cylindrical mandrel with little or no taper. The rolls are driven by rack and pinion gears of different radii along profiled cams, completing multiple 360º rotations around the tube.
Cold rolling is a very precise method of reducing very thin walled and/or smaller diameter tubes, and is often used as the final cold working step. By rolling, we’re able to achieve exceptional control over dimensional tolerances and surface finish while also minimizing material loss and improving the metal’s microstructure.
Because it uses compression, tube rolling is well suited to processing unique metals like titanium and zirconium alloys.
Our cold rolling capabilities include both classic 2-roll (single roll set) tube rollers and an advanced 3-roll approach.
Cold Drawing
Typically used as the first form of size reduction for seamless tubes, cold drawing reduces the diameter by pulling the tube through a die that is smaller than the tube. In order to fit the tube into the die, one end is ‘swaged’ or ‘tagged’ thereby reducing the diameter of the leading end before drawing. Next, the narrowed end is passed through the die and clamped to a drawing trolley which pulls the tube through the die. After drawing the ‘tag’ is cropped from the tube end prior to cleaning.
Sink drawing
This is the simplest of the three drawing methods, as there is no tooling to support the ID surface. The tube is drawn through a die made of polished tool steel or industrial diamond, thereby reducing its inside and outside diameters. Our specialized lubrication and application techniques, combined with our proprietary die profiles, enable the OD surface to become smoother as the tube is drawn. Since the inside diameter is not constrained, the wall thickness of the tube will normally increase during drawing, and the ID surface finish will normally become rougher during a sink draw.
Rod drawing
Rod drawing is our most commonly used cold draw method, primarily for intermediate or in-process drawing stages, where both the outside diameter and wall thickness are reduced at the same time.
The tube is loaded over a hardened steel mandrel rod and both are then drawn through a die. This squeezes the tube onto the rod, reducing the outside diameter and thinning the wall simultaneously. The die and mandrel determine the size of the drawn tube, which is then slightly expanded by applying pressure to the outside of the tube so that the rod can be removed. Since larger reductions in cross-sectional area can be achieved by rod drawing, this method is used for mid-process stages to reduce tube sizes prior to the final drawing cycle.
Plug drawing
This type of drawing is used to achieve the best possible surface finish and the greatest control over both dimensions and final temper. The outside diameter and wall thickness of the tube are both reduced during plug drawing, as the tube travels through a die and over a stationary plug/mandrel made of high grade tool steel. The plug or mandrel has a polished surface and is attached to a fixed back rod, which is carefully positioned within the drawing die. The tube is loaded over the mandrel/back rod. As the tube passes through the die, the burnishing action of the metal flowing over the stationary plug imparts a high tolerance surface finish inside the tube.
When properly lubricated and prepared, the ID will show very few flaws and finishes of 16 RMS or better can be achieved. Plug drawing is normally chosen for the final draw stage because it achieves a high quality surface finish, exceptional dimensional control, and positive influence on tensile strength requirements.
Annealing
Annealing is used to soften the metal before further cold working or fabrication processes, and improves the overall metallurgical microstructure of the tube. During tube reduction or cold drawing, it can become hard and somewhat brittle. To be able to draw the tube again, stresses formed during cold working need to be removed to return the material to its normal state.
During annealing the tube is heated to a controlled temperature (up to 2100°F) and soak time. Through this process the tube remains in shape, but the grains in the structure of the tube reform into a regular unstressed pattern. The resulting annealed tube is softer and suitable for redrawing.
Our closely controlled annealing and heat treat processes are audited regularly by our nuclear, medical, and aerospace customers.
Straightening
Drawing and annealing generally results in some degree of bowing, producing a slight bend in the tubing. We use multiple roll mechanical straighteners in the first stage of finishing. The straightener applies pressure and flex to the product in order to remove bends or bows, resulting in a straightness level of 0.010” per foot, or better. Straightening can introduce slight changes to the size and mechanical properties of the tubing, so these aspects are very carefully controlled during the process.
There are probably hundreds of different methods for packing stainless pipe, and most of them have merit, but there are two principles that are vital for any method to work prevent rusting and Sea transportation security.


We inventory stainless steel grades that are readily used in manufacturing such as 304, 304L and 316/L to harder to find items such as 309H, 330 or 405 stainless.



Stainless steel pipe (tube) has excellent characteristics of corrosion resistance and smooth finishing. Stainless steel pipe (tube) is commonly used in demanding equipment like automobiles, food processing, water treatment facilities, oil and gas processing, refinery and petrochemicals, breweries and energy industries.

Stainless steel tube is typically measured by its outer diameter and can be used in a variety of applications including a number of structural applications. Stainless steel tubing is extremely durable and able to withstand corrosion. This tubing will not rust, even if exposed to the elements, heat, and other extreme conditions. Because of these factors, stainless steel tubing can be used for a wide variety of applications.
The stainless steel tubing that is supplied by SunnySteel can used in a variety of industries, including:
Considering the importance of outside and inside surface of stainless steel tubes for fluid power industry, Our mills are providing tubes that are free from scale, rust, seams, laps.
the main requirement for stainless steels is that they should be corrosion resistant for a specified application or environment. The selection of a particular “type” and “grade” of stainless steel must initially meet the corrosion resistance requirements.
Additional mechanical or physical properties may also need to be considered to achieve the overall service performance requirements.
Need to inquire about our products? Fill out the form below and our staff will be in touch!
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: The delivery time of customized products is generally 25 35 days, and non customized products are generally shipped within 24 hours after payment.
Q: Do you provide samples? Is it free?
A: If the value of the sample is low, we will provide it for free, but the freight needs to be paid by the customer. But for some high value samples, we need to charge a fee.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: T/T 30% as the deposit,The balance payment is paid in full before shipment
Q: What is the packaging and transportation form?
A: Non steaming wooden box and iron frame packaging. Special packaging is available according to customer needs. The transportation is mainly by sea.
Q: What is your minimum order quantity?
A: There is no minimum order quantity requirement. Customized products are tailor made according to the drawings provided by the customer.