Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199
Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199

A106 seamless pipe, also called A106 seamless pressure pipe, in various sizes and profiles. This pipe is commonly specified for applications where piping is used to transport fluids and gasses at high temperatures and/or pressures. A106 seamless pressure pipe a key component in power plants, oil and gas refineries, petrochemical processing plants, boilers, and more.
A106 seamless pipe, also called A106 seamless pressure pipe, in various sizes and profiles. This pipe is commonly specified for applications where piping is used to transport fluids and gasses at high temperatures and/or pressures. A106 seamless pressure pipe a key component in power plants, oil and gas refineries, petrochemical processing plants, boilers, and more. The ASTM A106 pipe of Grade B is a seamless carbon steel specification that works in high temperature services. ASTM A106 Grade B pipe is designed with a chemical composition of chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and other constituting alloys. The A106 pipe has excellent corrosion resistance properties and works well across different oxidative environments.
The ASTM A106 Gr.B Material is designed having excellent mechanical properties. This material has a minimum tensile strength of 60,000psi with a minimum yield strength of 35,000psi. The A106 Gr B pipe of this specification is well suited for bending, flanging, and different forging operation. The A106 pipe suppliers can supply the pipes in seamless, welded, and erw specifications.
An A106 gr.b grade pipe is designed in sizes of NPS 1/8 to NPS 48. The pipe is designed in schedules of SCH 20 through XXH. The SA 106 Gr B works well in higher temperatures and can be either hot or cold rolled. The pipes have plain, bevelled, and threaded ends.
ASTM A106 Grade B is a mild steel pipe material usually used in industrial plants, power plants, power plants, refineries, and chemical plants. ASTM A106 GR. B Carbon Steel Seamless pipes must be solution annealed according to the heat treatment part to restore the ferrite.
A106 pipe has three grades: Grade A and Grade B and C, where in most circumstances used for Grade B.
ASTM A106 pipe (also covered in ASME specifications as S/A 106) is the standard specification for seamless carbon steel pipe for high-temperature service. Most common uses are in refineries and plants when gasses or fluids are transported at high temperatures and pressures.
| Grade | C≤ | Mn | P≤ | S≤ | Si≥ | Cr≤ | Cu≤ | Mo≤ | Ni≤ | V≤ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A106 GradeA | 0.25 | 0.27-0.93 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.4 | 0.08 |
| ASTM A106 GradeB | 0.3 | 0.29-1.06 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.4 | 0.08 |
| ASTM A106 GradeC | 0.35 | 0.29-1.06 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.4 | 0.08 |
| Grade | Rm Mpa Tensile Strength | Yield Point (Mpa) | Elongation | Delivery Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A106 GradeA | ≥330 | ≥205 | 20 | Annealed |
| ASTM A106 GradeB | ≥415 | ≥240 | 20 | Annealed |
| ASTM A106 GradeC | ≥485 | ≥275 | 20 | Annealed |
| JIS | ASTM | BS | DIN | NF | ISO | Index Number | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Std.No | Grade | Type | Std.No | Grade | Type | Std.No | Grade | Type | Std.No | Grade | Type | Std.No | Grade | Type | Std.No | Grade | Type | |
| JIS G3456 | STPT370 | C | ASTM A106 | GrA | C | 3602 | HFS360 | C | 17175 | St35.8 | C | A49-211 | TU37b | C | 2604-02-01 00:00:00 | TS5 | C | C004 |
| (STPT38) | " | CFS360 | C | 17177 | St37.8 | C | A49-213 | TU37c | C | 2604-03-01 00:00:00 | TW9H | C | ||||||
| " | ERW360 | C | A49-243 | TU37c | C | |||||||||||||
| " | CEW360 | C | ||||||||||||||||
| STPT410 | C | ASTM A106 | GrB | C | 3602 | HFS410 | C | 17175 | St45.8 | C | A49-211 | TU42b | C | 2604-02-01 00:00:00 | TS9H | C | ||
| (STPT42) | " | CFS410 | C | 17177 | St42.8 | C | A49-213 | TU42c | C | |||||||||
| " | ERW410 | C | A49-243 | TU42c | C | |||||||||||||
| " | CEEW410 | C | ||||||||||||||||
| STPT480 | C | ASTM A106 | GrC | C | 3602 | HFS460 | C | A49-211 | TU48b | C | 2604-02-01 00:00:00 | TS14 | C | |||||
| (STPT42) | " | CFS460 | C | A49-213 | TU48c | C | ||||||||||||
| " | ERW460 | C | ||||||||||||||||
| " | CEEW460 | C | ||||||||||||||||
Lengths
Lengths required shall be specified on order. No “jointers” permitted unless otherwise specified. If no definite lengths required, following practice applies: Single Random — 17′ ~ 24′ lengths Double Random — 36′ ~ 44′ lengths
Required Markings on Each Length
(On Tags attached to each Bundle in case of Bundled Pipe) Rolled, Stamped, or Stenciled (Mfrs. Option) Manufacturer’s name or brand. Length of pipe. A106 A, A 106 B, A 106 C. ANSI schedule number. Hydrostatic test pressures and/or NDE; Weight per foot (NPS 4 and larger) or NH if neither is specified. Additional “S” if tested supplementary requirements.
Lining and coating on the A106 Steel pipe is done to protect the surface of the pipe against corrosion and different affluents. The coated A106b pipe helps in coating the outer surface of the material. They prevent contaminants from entering the piping structures. A lined SA 106 gr b pipe covers the interior surface of a pipe or other structures. The lining is performed in structures that transport volatile liquids and gases.
The A106 galvanized pipe is dipped into a protective zinc coating to prevent the formation of corrosion and rust. The galvanized A106 carbon steel pipe offers complete protection and is easy to clean and inspect.
| ize | Other Diameter | WT | Pipe I.D. | Gallon | Standard to XXHY | Section Modulus | Weight | Schedule Pipe # |
| 3/4 | 1.05 | 0.113 | 0.824 | .0277 | STD | .0705 | 1.13 | 40 |
| 0.219 | 0.612 | .0153 | .1006 | 1.95 | 160 | |||
| 0.154 | 0.742 | .0225 | XHY | .0853 | 1.48 | 80 | ||
| 1/2 | 0.84 | 0.109 | 0.622 | .0158 | STD | .0407 | 0.85 | 40 |
| 0.188 | 0.464 | .0088 | .0528 | 1.31 | 160 | |||
| 0.147 | 0.546 | .0122 | XHY | .0478 | 1.09 | 80 | ||
| 1 1/4 | 1.66 | 0.140 | 1.380 | .0777 | STD | .2346 | 2.27 | 40 |
| 0.250 | 1.160 | .0549 | .3421 | 3.77 | 160 | |||
| 0.191 | 1.278 | .0666 | XHY | .2913 | 3.00 | 80 | ||
| 1 | 1.315 | 0.133 | 1.049 | .0449 | STD | .1328 | 1.68 | 40 |
| 0.250 | 0.815 | .0271 | .1904 | 2.85 | 160 | |||
| 0.179 | 0.957 | .0374 | XHY | .1606 | 2.17 | 80 | ||
| 2 | 2.375 | 0.109 | 2.157 | .1898 | .4205 | 2.64 | 10 | |
| 0.154 | 2.067 | .1743 | STD | .5606 | 3.66 | 40 | ||
| 0.344 | 1.687 | .1161 | .9806 | 7.47 | 160 | |||
| 0.281 | 1.813 | .1344 | .8666 | 6.29 | ||||
| 0.218 | 1.939 | .1534 | XHY | .7309 | 5.03 | 80 | ||
| 0.250 | 1.875 | .1434 | .8045 | 5.68 | ||||
| 1 1/2 | 1.90 | 0.145 | 1.610 | .1058 | STD | .3262 | 2.72 | 40 |
| 0.281 | 1.338 | .0730 | .5079 | 4.86 | 160 | |||
| 0.200 | 1.500 | .0918 | XHY | .4118 | 3.63 | 80 | ||
| 3 | 3.50 | 0.120 | 3.260 | .4336 | 1.0411 | 4.34 | ||
| 0.156 | 3.188 | .4147 | 1.3122 | 5.58 | ||||
| 0.188 | 3.124 | .3984 | 1.5342 | 6.66 | ||||
| 0.438 | 2.624 | .2811 | 2.8774 | 14.34 | 160 | |||
| 0.172 | 3.156 | .4064 | 1.4265 | 6.12 | ||||
| 0.300 | 2.900 | .3431 | XHY | 2.2253 | 10.26 | 80 | ||
| 0.216 | 3.068 | .3840 | STD. | 1.7241 | 7.58 | 40 | ||
| 0.250 | 3.000 | .3672 | 1.9372 | 8.69 | ||||
| 0.281 | 2.938 | .3521 | 2.1207 | 9.67 | ||||
| 2 1/2 | 2.875 | 0.120 | 2.635 | .2833 | .6870 | 3.53 | 10 | |
| 0.250 | 2.375 | .2301 | 1.2468 | 7.02 | ||||
| 0.203 | 2.469 | .2487 | STD. | 1.0640 | 5.80 | 40 | ||
| 0.216 | 2.443 | .2435 | 1.1169 | 6.14 | ||||
| 0.276 | 2.323 | .2202 | XHY | 1.3386 | 7.67 | 80 | ||
| 0.375 | 2.125 | .1842 | 1.6371 | 10.02 | 160 | |||
| 3 1/2 | 4.0 | 0.120 | 3.760 | .5768 | 1.3776 | 4.98 | 10 | |
| 0.318 | 3.364 | .4617 | XHY | 3.1400 | 12.52 | 80 | ||
| 0.226 | 3.548 | .5136 | STD. | 2.3939 | 9.12 | 140 | ||
| 0.250 | 3.500 | .4998 | 2.6001 | 10.02 | ||||
| 0.281 | 3.438 | .4821 | 2.8562 | 11.17 |
A53 pipe is best suited for transport of air, water, steam and oil in low- and medium pressure applications across the industrial spectrum. It’s also commonly used as structural steel. A106 pipe is formulated specifically for high-temperature and high-pressure service, usually in power generation applications.
What is the difference between the material specifications for A106 Grade B Seamless pipe and A53 Grade B (Type S) seamless pipe?
We are sometimes asked this question by Customers and whether or not they are interchangeable. This article will focus on comparing the three most commonly requested ones- A106B, A106C and A53B seamless and will highlight some of the key factors an engineer would focus on in their selection process.
First and foremost, let’s start with the most important concept – suppliers and manufacturers must always follow the designated requirements and specifications invoked for a specified line item or order.
A customer must exercise caution when evaluating these specifications to allow proper selection between these two materials. For starters, a visual inspection of the pipe will determine whether or not the pipe is seamless or welded, but it will not reveal which specification.
A106 is only produced as a seamless product and is available in three grades; A, B, C. There are no Types in A106 because it is produced only as a seamless product.
A53 comes in two grades and three types. A53 can be produced as a seamless product (A53 Grade A Type S (Seamless) and A53 Grade B Type S (Seamless) or as a welded product (A53 Grade B Type E (Welded), A53 Grade A Type E (Welded) or A53 Grade A Type F (Welded)).

Seamless pipe is often made by drawing a solid shape over a mandrel to form the configuration of a tube. Welded pipe is more commonly made by rolling a flat strip of material into a tube and joining the edges together with a longitudinal weld. The weld can be made by either Electric Resistance Welding (Type E) or by Furnace Butt Welded/Continuous Welding (Type F).
The ASTM A106 specification is for seamless carbon steel pipe for High-Temperature Service. A106 must be produced with killed steel. It covers nominal pipe sizes (NPS) 1/8” NPS to 48 NPS”. For sizes 1- 1/2” NPS and under, A106 may be produced by two different processes; either hot finished or cold drawn. Unless otherwise specified, pipe 2″ NPS and over shall be furnished hot finished. Typical uses for A106 are for handling liquids and gasses at high temperatures and pressures in power plants, oil refineries, and industrial facilities.
The ASTM A53 specification is for steel pipe of welded or seamless construction, and available in black or hot-dipped zinc-coating (aka galvanized) 3. A53 does not require the use of killed steel as a starting material. It covers nominal pipe sizes 1/8” NPS to NPS 26” NPS. It is incumbent upon a purchaser to request the grade and type, whether black or galvanized, and the desired end configuration. A53 does not require nor prohibit any specific process (such as hot finished or cold drawn or other process) in the production of seamless pipe. Typical uses of A53 pipe are structural applications or for low pressure fluid systems such as air, gas, and water.
Since A106 seamless can be hot finished or cold drawn, in very, very basic terms the difference between the two is a matter of the temperature at which the process is performed. Hot finished pipe is produced at temperatures over about 1700F° while cold drawn is produced at much lower temperatures and with more processing. In general, cold drawn pipe has an improved surface finish and better dimensional control.
As one can see in the Chemical Composition Chart below it is first important to identify the actual specifications and grades by the revision years to effectively compare. Here we will compare the ASTM A106-15 in both the B and C grades to ASTM A53-12 Grade B in Type S (Seamless).
As one can see in the charts below, there are no major differences in chemistry and mechanical properties that would prevent a mill from producing a pipe that will meet these requirements of A106 Grade B and A53 Grade B Type S (Seamless).
Now let’s look at the chemistry nuances as there is a more to review. First, the specified elements within the two specifications are not the same. A53B does not have a requirement for minimum silicon content (although silicon can be present); for A106, however, the minimum silicon content is 0.10%. Silicon is regarded as an important element for improving the heat resistance ability. The manganese, phosphorous and sulfur requirements are different, but the maximums are quite high and material rarely approaches these values. The remaining elements are the same for the B grades.
As for the mechanical properties, A106-15 Grade B and A53-12 Grade B Seamless have the same tensile strength, yield strength and the same elongation values in 2” NPS when tested with a longitudinal strip test specimen.
What then are the differences between A106 grades B and C?6 The maximum allowable carbon content is higher in Grade C; which can result in higher mechanical properties due to this increased carbon content. An engineer may be interested in this higher tensile and yield strength provided by Grade C when selecting materials for high temperature service.
Regarding the need for heat treatment, the only requirements are A106 requires cold drawn material to be stress relieved at 1200°F or higher. A53 Grades A and B seamless products do not require heat treatment at all.
Additional points where differences exist between A106 and A53 include weight, dimensions, and end finish. For A53, the weight of any pipe shall not vary more than 10% from its specified weight. For A106, the mass of any length of pipe shall not vary more than 10% over and 3.5% under that specified.
Dimensions are different and may be more restrictive in either specification; depending on the ordered size in NPS. Please refer to the Dimensions Chart below for specific tolerances for the outside diameter. A53 and A106 have the same wall thickness tolerance; the minimum wall at any point shall not be more than 12.5% under the specified wall thickness.
The end finish for A106 pipe 1-1/2” NPS and less for all wall thicknesses shall be plain end square cut or plain end beveled at the option of the manufacturer. For A106 pipe of 2” NPS and larger, walls through extra strong shall be plain end beveled, and walls over extra strong shall be plain end square cut. Threaded ends are not an available option.
Available end finishes in A53 are plain end or threaded. Plain ends may be either beveled or square cut. For 1-1/2” NPS and less, the end finish is the option of the manufacturer unless otherwise specified. 2” NPS and larger pipe of standard or extra strong weight, or wall thickness less than .500” (except double extra- strong) shall be plain end beveled. Pipe with a specified wall thickness greater than .500” and all double extra-strong pipe shall be plain end square cut. Threaded ends are available and may be ordered with couplings.
Dual certification occurs when a manufacturer produces pipe that meets the more stringent requirements between the specifications involved; including, but not limited to, melt practice and processing, chemistry control, dimensions, and weight per length. It is easy to understand, therefore, how it is possible for a mill to dual certify pipe as A106 Grade B and A53 Grade B Type S (Seamless); or even triple certify as A106 Grade B/C and A53 Grade B Type S (Seamless)
Not surprising, it is common for a customer (be it a purchasing professional or engineer) to request A106 as an alternative to A53 seamless. Based on a customer’s review and decision-making and that the requirement is not for galvanized pipe, we can provide this alternative.
Chemical Composition Chart:
| Standard | Grade | Process | Chemical Composition % | |||||||||
| C max | Mn* | P max | S max | Si min | Cr˟ max | Cu˟ max | Ni˟ max | Mo˟ max | V˟ max | |||
| ASTM A106-15 | B | SMLS | 0.30* | 0.29-1.06 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.08 |
| ASTM A106-15 | C | SMLS | 0.35* | 0.29-1.06 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.08 |
| ASTM A53-12 | B | SMLS | 0.30* | 1.20 | 0.05 | 0.045 | — | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.08 |
| * | For each reduction of 0.01% below the specified carbon maximum, an increase of 0.06% manganese above the specified maximum will be permitted up to a maximum of 1.65%. |
| x | The sum of these five elements shall not exceed 1% (1.00% for A53) |
| — | No requirement for this element |
Mechanical Properties Chart:
| Standard | Grade | |||||
| Process | Tensile Strength (MPa) Min | Yield Strength (MPa) Min | Elongation in 2” (%) MinimumLong. Strip Test | Elongation in 2” (%) MinimumTrans. Strip Test | ||
| ASTM A106-15 | B | SMLS | 60,000 [415] | 35,000 [240] | 30 | 16.5 |
| ASTM A106-15 | C | SMLS | 70,000 [485] | 40,000 [275] | 30 | 16.5 |
| ASTM A53-12 | B | SMLS | 60,000 [415] | 35,000 [240] | 30 | See Spec |
Dimensions Chart:
| Standard | Permissible Variations in Outside Diameter | ||
| NPS” | OVER | UNDER | |
| ASTM A53-12 | 1-1/2 and less | 1/64” (0.015”) | 1/64” (0.015”) |
| ASTM A53-12 | 2 and over | 1% of OD | 1% of OD |
| ASTM A106-15 | 1/8 to 1-1/2 | 1/64” (0.015”) | 1/64” (0.015”) |
| ASTM A106-15 | Over 1-1/2 to 4 | 1/32” (0.031”) | 1/32” (0.031”) |
| ASTM A106-15 | Over 4 to 8 | 1/16” (0.062”) | 1/32” (0.031”) |
| ASTM A106-15 | Over 8 to 18 | 3/32” (0.093”) | 1/32” (0.031”) |
| ASTM A106-15 | Over 18 to 26 | 1/8” (0.125”) | 1/32” (0.031”) |
| ASTM A106-15 | Over 26 to 34 | 5/32” (0.156”) | 1/32” (0.031”) |
| ASTM A106-15 | Over 34 to 48 | 3/16” (0.187”) | 1/32” (0.031”) |
The production of our seamless pipes is tightly regulated and all of the pipes we stock have been fully tested to international standards to ensure we only supply the highest quality products.
| Product name | Executive standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel code/ Steel grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black and Hot-dipped Zinc-coated Steel Pipes Seamless | ASTM A53 | 0.3-1200 x 1.0-150 | GR.A, GR.B, GR.C |
| Seamless Carbon Steel for High Temperature Service | ASTM A106 | 10.3-1200 x 1.0-150 | GR.B, GR.C |
| Seamless Cold-drawn Low-Carbon Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser Tubes | ASTM A179 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | Low Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Carbon Steel Boiler Tubes for High Pressure | ASTM A192 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | Low Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Cold-drawn Intermediate Alloy Steel Heat-exchanger and Condenser Tubes | ASTM A199 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | T5, T22 |
| Seamless Medium-carbon Steel Boiler and Superheater Tubes | ASTM A210 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | A1, C |
| Seamless Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy Steel Boiler, Superheater and Heat-exchanger Tubes | ASTM A213 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | T5, T5b, T9 , T11, T22 ,T91 |
| Seamless Carbon and Alloy Steel for Mechanical Tubing | ASTM A333 | 1/4"-42" x SCH20-XXS | Grade1 Gr. 3,Gr..6, Gr.8 , Gr. 9 |
| Seamless Cold-drawn Carbon Steel Feedwater Heater Tubes | ASTM A556 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | A2, B2 |
| Round and shaped steel cold formed welded and seamless carbon steel structural pipe. | ASTM A500 | OD :10.3-820 x 0.8- 75 | Grade A, B, C, D |
| Carbon and alloy steel mechanical tubing, either hot-finished or cold-finished | ASTM A519 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | 1020, 1025, 4130, 4140 |
| For seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe for high-temperature service | ASTM A335 | 1/4"-42" x SCH20-XXS | A/SA 335 P1, P2, P11, P12, P15, P22, P91, P92, P122 |
Cold Drawn Seamless Mechanical Tubing (CDS) is a cold drawn 1018/1026 steel tube which offers uniform tolerances, enhanced machinability and increased strength and tolerances compared to hot-rolled products.

Cold drawn steel tube is with hot-rolled steel coil as raw material, and tandem cold rolling pickled to remove oxide scale, its finished rolling hard roll, rolling hard volumes due to the continuous cold deformation caused by cold hardening strength, hardness increased indicators declined tough plastic, stamping performance will deteriorate, which can only be used for simple deformation of the parts.
Rolling hard roll can be used as the raw material of the hot-dip galvanizing plant, hot dip galvanizing line set annealing line. Rolling hard roll weight is generally 6 to 13.5 tons, the coil diameter of 610mm.
Hot-rolled seamless steel pipe production base deformation process can be summarized as three stages: perforation, extension and finishing.
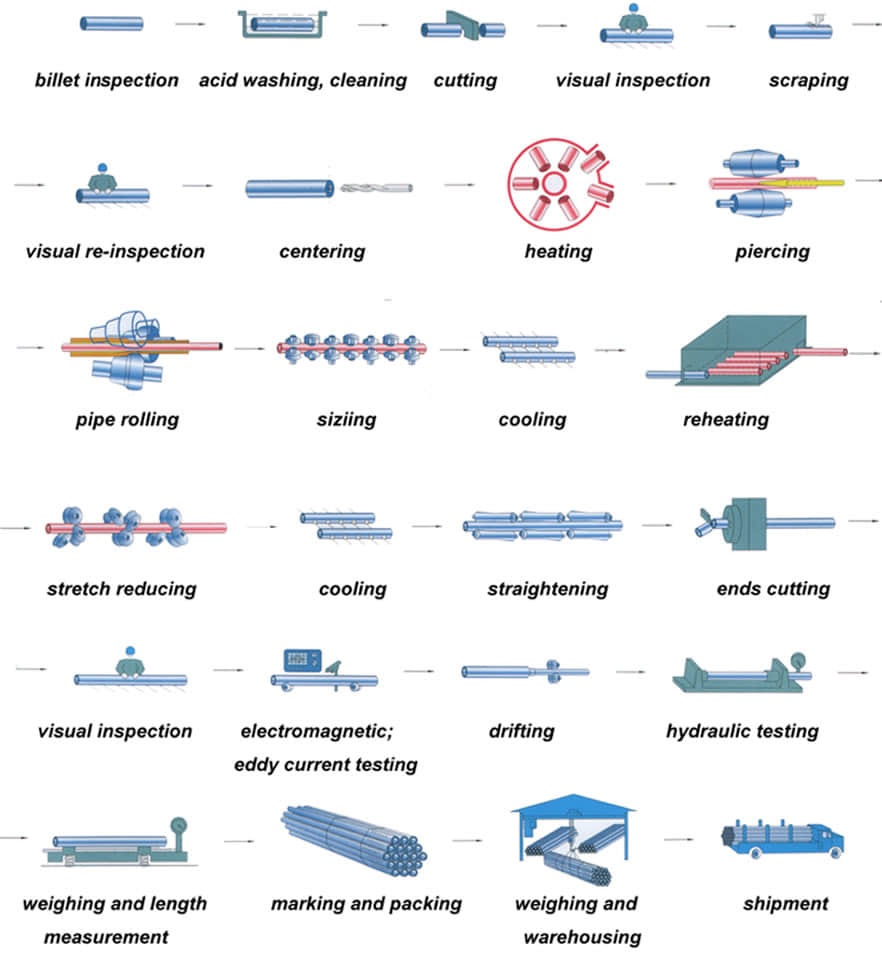
The main purpose of the perforation process is to become a solid round billet piercing hollow shell. Capillary in the specifications, accuracy and surface quality can not meet the requirements of the finished product, further improvements are needed to deform the metal through. The main purpose of the stretching machine is further reduced sectional view (main compression wall) for a larger axial extension, so that the capillary improved dimensional accuracy, surface quality and organizational performance.
After stretching machine rolled steel pipe shortage collectively need further molding mill in order to achieve the requirements of the finished pipe. Rolled steel due to pass in the method widely used in the production of seamless steel tubes.
So far, due to the method pass rolling steel can be divided into two categories: core pension without rolling rolling (hollow body rolling), and with the mandrel. Sizing machines, reducing mill and stretch reducing mill belonging to the hole without mandrel type continuous rolling mills are generally coffin. Its main purpose is to reduce the diameter of the deformation process or sizing get finished steel, the wall thickness of process control, can make thinning, thickening or nearly unchanged.
All the traditional hole-type rolling machine with mandrel belong to extend machine. The main purpose is to reduce the deformation process perforated capillary wall thickness and outer diameter roll passes in the deformation zone and the mandrel posed, for a larger axial extension. At the same time a certain improvement in the organization, performance, accuracy, surface quality.

Before cutting pipe and tubing
No matter the material, measure the diameter of the pipe or tube to be cut to ensure that you use the right-size tube cutter for the job. When determining how to make a straight cut, use a tape measure and a pencil or other writing instrument to mark on the surface where you want to cut. If possible, mark around the circumference of a pipe, especially when cutting with a handsaw. Ensure that a cut is as straight as possible by securing the pipe with a vise, clamp, miter box or even duct tape to keep the length from shifting out of place while cutting.
After cutting pipe and tubing

Geometrical inspection of steel pipes The outer diameter, wall thickness, bending and length of the steel pipe can be inspected on the inspection table with an outer caliper, a micrometer and a bending ruler, and a length tape measure.
Take seamless steel pipe as an example, there are some tolerances that affect quality. Noting this, and you will get a better pipe.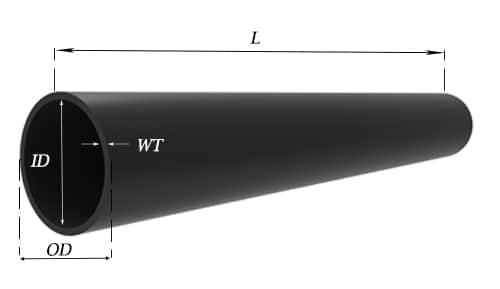
Weight tolerance
For pipe NPS 12 (DN300, 323.8mm) and under, the weight shall vary within -3.5% / +10%.
For pipe over NPS 12 (DN300, 323.8mm), the weight shall vary within -5% / +10%.
Pipe of NPS 4 (DN100, 114.3mm) and smaller may be weighed in convenient lots; pipe in sizes larger than NPS 4 shall be weighed separately.
Quantity tolerance
Normally mills take -10% to +10% tolerance, but TPMCSTEEL keeps ±3% variation.
Length tolerance
For Seamless pipe& tube, if definite cut lengths are ordered, the length shall vary within -0mm / +6mm.
| Pipe types | Pipe Szie(mm) | Tolerances | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot rolled | OD | <50 | ±0.50mm |
| ≥50 | ±1% | ||
| WT | <4 | ±12.5% | |
| ≥4-20 | +15%, -12.5% | ||
| >20 | ±12.5% | ||
| Cold drawn | OD | 6-10 | ±0.20mm |
| 10-30 | ±0.40mm | ||
| 30-50 | ±0.45 | ||
| >50 | ±1% | ||
| WT | <1 | ±0.15mm | |
| >1-3 | + 15%, – 10% | ||
| >3 | + 12.5%, – 10% | ||
| Standard | Hot finished seamless tube | Cold flnished seamless tube | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Out diameter (mm) | Tolerance | Out diameter (mm) | Tolerance | |
| EN10216-1 | ≤100 | +/-0.75% (min.+/-0.5mm) | All | +/-0.5% |
| EN10216-2 | (min. +/-0.30mm) | |||
| DIN17175 | >100 | +/-0.90% | ||
| GB/T 3087 | ≤460 | +/-0.75% (min.+/-0.5mm) | 10-30 | +/-0.40mm |
| >30-50 | +/-0.45mm | |||
| >50 | +/-1.0% | |||
| GB/T 5310 GB/T 9948 GB/T 6479 | <57 | +/-0.40mm | ≤30 | +/-0.20mm |
| 57-325 | +/-0.75% | >30-50 | +/-0.30mm | |
| >325-460 | +1%,-2mm | >50 | +/-0.8% | |
| ASME SA-179M ASME SA-192M ASME SA-209M ASME SA-210M ASME SA-213M JIS G 3461 JIS G 3461 | ≤101.6 | +0.4, -0.8mm | <25.4 | +/-0.10mm |
| >25.4-38.1 | +/-0.15mm | |||
| >38.1-50.8 | +/-0.20mm | |||
| 101.6-190.5 | +0.4, -1.2mm | >50.8-63.5 | +/-0.25mm | |
| >63.5-76.2 | +/-0.30mm | |||
| >76.2 | +/-0.38mm | |||
| ASME SA106 ASME SA335 | ≤48.3 | +/-0.40mm | ≤48.3 | +/-0.40mm |
| 48.3-114.3 | +/-0.79mm | |||
| 114.4-219.1 | +1.59, -0.79mm | |||
| 219.2-323.9 | +2.38, -0.79mm | >48.3 | +/-0.79mm | |
| >324 | +/-1.0% | |||
| Standard | Hot finished seamless tube | Cold flnished seamless tube | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIN17175 | Out diameter OD(mm) | Wall thickness T(mm) | Tolerance | Out diameter (mm) | Wall Thickness T(mm) | Tolerance |
| ≤130 | S≤2Sn | +15%, -10% | -- | All | +/-10% (min. +/-0.2mm) |
|
2Sn| +12.5%, -10% |
| |||||
| S>4Sn | +-/9% | |||||
| >130 | S≤0.05da | +17.5%, -12.5% | ||||
0.05da| +/-12.5% |
| |||||
| S>0.11da | +/-10% | |||||
| EN 10216-1 EN 10216-2 | ≤219.1 | - | +/-12.5% (min.+/-0.4mm) |
|||
| -- | T/D≤0.025 | +/-20% | ||||
0.025| +/-15% |
| |||||
0.05| +/-12.5% |
| |||||
0.1| +/-10% |
| |||||
| GB/T 3087 | -- | ≤20 | +15%,-12.5% (min.+0.45, -0.35mm) | -- | 1.0-3.0 | +15%, -10% |
| >20 | +/-12.5% | -- | >3 | +12.5%, -10% | ||
| GB/T 5310 GB/T 9948 GB/T 6479 | -- | <4.0 | +15%,-10% (min.+0.48, -0.32mm) | -- | 2-3 | +12%,-10% |
| 4-20 | +12.5%,-10% | >3 | +/-10% | |||
| >20 | +/-10% | |||||
| ASME SA-179M ASME SA-192M ASME SA-209M ASME SA-210M ASME SA-231M JIS G 3461 JIS G 3462 | -- | 2.41-3.8 | +35%, -0% | ≤38.1 | -- | +20%,-0% |
| 3.8-4.6 | +33%,-0% | >38.1 | -- | 22%,-0% | ||
| >4.6 | +28%,-0% | -- | -- | -- | ||
| ASME SA-106 ASME SA-335 | -- | All | +/12.5% | All | +/-10% | |
Note:

Positive material identification (PMI) testing is the examination of a material, usually a metallic alloy, to confirm the material is consistent with the user’s request.
Steel pipe delivery status(condition): cold / hard (BK), cold / soft (BKW), after cold stress relief annealing (BKS), annealing (GBK), normalized (NBK).
| Term | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-finished/hard (cold-finished as-drawn) | BK | No heat treatment after the last cold-forming process. The tubes therefore have only low deformability. |
| Cold-finished/soft (lightly cold-worked) | BKW | After the last heat treatment there is a light finishing pass (cold drawing) With proper subsequent processing, the tube can be cold-formed (e.g. bent, expanded) within certain limits. |
| Annealed | GBK | After the final cold-forming process the tubes are annealed in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
| Normalized | NBK | The tubes are annealed above the upper transformation point in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
There are probably hundreds of different methods for packing a pipe, and most of them have merit, but there are two principles that are vital for any method to work prevent rusting and Sea transportation security.
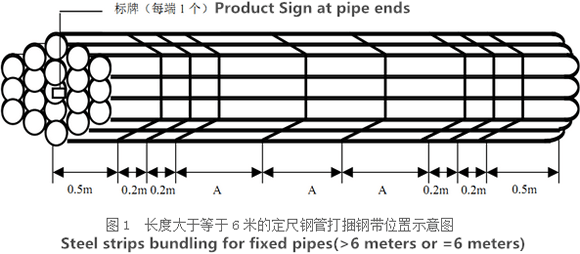
Our packing can meet any needs of the customers.
Need to inquire about our products? Fill out the form below and our staff will be in touch!
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: The delivery time of customized products is generally 25 35 days, and non customized products are generally shipped within 24 hours after payment.
Q: Do you provide samples? Is it free?
A: If the value of the sample is low, we will provide it for free, but the freight needs to be paid by the customer. But for some high value samples, we need to charge a fee.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: T/T 30% as the deposit,The balance payment is paid in full before shipment
Q: What is the packaging and transportation form?
A: Non steaming wooden box and iron frame packaging. Special packaging is available according to customer needs. The transportation is mainly by sea.
Q: What is your minimum order quantity?
A: There is no minimum order quantity requirement. Customized products are tailor made according to the drawings provided by the customer.