Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199
Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199

ASTM A333 Gr.8 Ultra-low temperature steel pipe is applicated for Ultra-low temperature service.
ASTM A333 Gr.8 Ultra-low temperature steel pipe is applicated for Ultra-low temperature service.
As the results of the experimental data, our factory successfully completed the grade of steel for Gr8 specifications for cryogenic Φ 355.6 x 50.8 mm pipe heat treatment.
The test results of tensile, impact work, hardness and flattening all meet the requirements of ASTM A333.
The Gr8(commonly known as 9%Ni) steel pipe is mainly used for the storage and transportation of liquefied natural gas, and is one of the most technologically advanced, difficult and value-added products in civil steel products.Because of its flammability and ultra-low temperature, the ultra-low temperature steel used for storage and transportation of liquefied natural gas must have the comprehensive characteristics of strength, thermal stress and strain, welding performance and corrosion resistance.Therefore, whether such products can be produced is an important symbol representing the overall technical level of a steel enterprise.The successful production of Gr8 cryogenic tube effectively expands the variety range of 720 units and lays a foundation for further development of the market.
A333 Gr8 cryogenic pipe is a brand in American ASTM standard, which is mainly used for storage and transportation of liquefied natural gas. It is one of the products with the highest technical level, difficulty and added value in civil steel products.Whether this kind of products can be produced successfully represents the overall technical level of an enterprise.In order to ensure this kind of steel pipe material requirement, valingheng steel has designed the steelmaking and smelting process in its own innovation.The test results of the steel pipe developed and produced show that the performance data of the steel pipe obtained by the heat treatment process are up to standard.
The Grade 8 steel involved is similar to AISI 4032 low alloy steel. ASTM A333 Grade 8 pipe shall be made by the seamless or welding process with the addition of no filler metal in the welding operation.



















Inspection and Test: Chemical Composition Inspection, Mechanical Properties Test(Tensile Strength,Yield Strength, Elongation, Flaring, Flattening, Bending, Hardness, Impact Test), Surface and Dimension Test,No-destructive Test, Hydrostatic Test.
Surface treatment: Oil-dip, Varnish, Passivation, Phosphating, Shot Blasting.
Both ends of each crate will indicate the order no., heat no., dimensions, weight and bundles or as requested.
Chemical Compositions(%)
| Compositions | Data |
| Carbon(max.) | 0.13 |
| Manganese | 0.90 max |
| Phosphorus(max.) | 0.025 |
| Sulfur(max.) | 0.025 |
| Silicon | 0.13-0.32 |
| Nickel | 8.40-9.60 |
| Chromium | … |
| Other Elements | … |
Mechanical properties
| Properties | PSI (Longitudinal) | MPa(Transverse) |
| Tensile strength, min, (MPa) | 100 000 | 690 |
| Yield strength, min, (MPa) | 75 000 | 515 |
| Basic minimum elongation for walls 5/16 in. [8mm] and over in thickness, strip tests, and for all small sizes tested in full section. | 22 | — |
| When standard round 2-in, or 50-mm gage length or proportionally smaller size test specimen with the gage length equal to 4D (4 times the diameter) is used | 16 | — |
| For strip tests, a deduction for each 1/32 in [0.8 mm] decrease in wall thickness below 5/16 in [8 mm] from the basic minimum elongation of the following percentage | 1.25 | — |
Elongation in 2 in or 50 mm, min, %:
|
Wall Thickness
|
Grade 8
|
||
|
in
|
mm
|
Longitudinal
|
Transverse
|
| 5/16 (0.312) | 8 | 22 | — |
| 9/32 (0.281) | 7.2 | 21 | — |
| 1/4 (0.250) | 6.4 | 20 | — |
| 7/32 (0.219) | 5.6 | 18 | — |
| 3/16 (0.188) | 4.8 | 17 | — |
| 5/32 (0.156) | 4 | 16 | — |
| 1/8 (0.125) | 3.2 | 15 | — |
| 3/32 (0.094) | 2.4 | 13 | — |
| 1/16 (0.062) | 1.6 | 12 | — |
IMPACT REQUIREMENTS
| Size of Specimen |
Minimum Average Notched Bar Impact Value of Each Set of Three Specimen
|
Minimum Notched Bar Impact Value of One Specimen only a Set
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ft-lbf
|
J
|
ft-lbf
|
J
|
|
| 10 by 10 | 13 | 18 | 10 | 14 |
| 10 by 7.5 | 10 | 14 | 8 | 11 |
| 10 by 6.67 | 9 | 12 | 7 | 9 |
| 10 by 5 | 7 | 9 | 5 | 7 |
| 10 by 3.33 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 4 |
| 10 by 2.5 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4 |
| Straight line interpolation for intermediate values is permitted. | ||||
the notched-bar impact properties of each set of three impact specimens, when tested at temperature specified shall be not less than the values prescribed.
IMPACT TEMPERATURE
|
Grade
|
Minimum Impact Test Temperature
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
°F
|
°C
|
|
|
8
|
-320
|
-195
|
MECHANICAL TESTING
Transverse or Longitudinal Tension Test and Flattening Test, Hardness Test, or Bend Test For material heat treated in a batch-type furnace, tests shall be made on 5% of the pipe from each treated lot. For small lots, at least one pipe shall be tested. For material heat treated by the continuous process, tests shall be made on a sufficient number of pipe to constitute 5% of the lot, but in no case less than 2 pipe. Hydrostatic Test Impact Test One notched bar impact test, consisting of breaking three specimens shall be made from each heat represtented in a heat-treatment load on specimens taken from the finished pipe.
HEAT TREATMENT REQUIREMENTS
All seamless and welded pipe shall be treated to control their microstructure by the following methods: Normalizing per A 333/A 333M-05 section 4.2.1.1; section 4.2.1.2 or section 4.2.1.3 Quenched and Tempered per A 333/A 333M – 05 section 4.2.2.1 Double Normalized and Tempered per A 333/A 333M – 05 section 4.2.2.2
IMPACT TEMPERATURE REDUCTION
|
Specimen Width Along Notch or Actual Material Thickness
|
Temperature Reduction , Degrees Colder
|
||
|
in
|
mm
|
°F
|
°C
|
| 0.394 | 10 (standard size) | 0 | 0 |
| 0.354 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.315 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.295 | 7.5 (3/4 std. size) | 5 | 3 |
| 0.276 | 7 | 8 | 4 |
| 0.262 | 6.67 (2/3 std. size) | 10 | 5 |
| 0.236 | 6 | 15 | 8 |
| 0.197 | 5 (1/2 std. size) | 20 | 11 |
| 0.158 | 4 | 30 | 17 |
| 0.131 | 3.33 (1/3 std. size.) | 35 | 19 |
| 0.118 | 3 | 40 | 22 |
| 0.099 | 2.5 (1/4 std. size) | 50 | 28 |
| Straight line interpolation for intermediate values is permitted. | |||
Gr. 8 contains 9% of Nickel, that is the most effective elements added to improve the steel toughness at low temperature to ensure its good toughness and high strength at low temperature down to – 195 ℃. Low temperature steel tube grade 8 is mainly used to produce device handling ethylene, propylene, urea, ammonia and compound fertilizer or process equipment washing, purification, desulfurization in pharmaceutical industry, degreasing and cryogenic equipment manufacturing, ultra-low temperature cold storage, transmission of liquefied gas pipe and tube components, such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cryogenic separation equipment, air separation equipment, etc.
ASTM A333 covers nominal (average) wall seamless and welded carbon and alloy steel pipe intended for use at low temperatures. Several grades of ferritic steel are included. Some product sizes may not be available under this specification because heavier wall thicknesses have an adverse affect on low-temperature impact properties.
A333 pipe is furnished to nine different grades designated by numbers 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, & 11.
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | Mo | V | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A333 Grade 1 | ≤0.30 | 0.40-1.06 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | |||||||
| ASTM A333 Grade 3 | ≤0.19 | 0.18-0.37 | 0.31-0.64 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | 3.18-3.82 | |||||
| ASTM A333 Grade 4 | ≤0.12 | 0.18-0.37 | 0.50-1.05 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | 0.44-1.01 | 0.47-0.98 | 0.40-0.75 | 0.04-0.30 | ||
| ASTM A333 Grade 6 | ≤0.30 | ≥0.10 | 0.29-1.06 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | ||||||
| ASTM A333 Grade 7 | ≤0.19 | 0.13-0.32 | ≤0.90 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | 2.03-2.57 | |||||
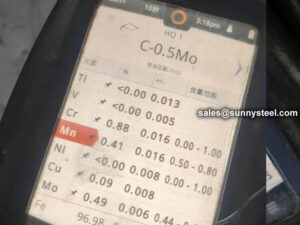
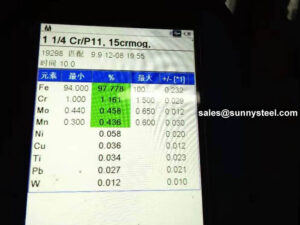
| ASTM A333 Gr. 8 | ≤0.13 | 0.13-0.32 | ≤0.90 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | 8.40-9.60 | |||||
| ASTM A333 Grade 9 | ≤0.20 | 0.40-1.06 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | 1.60-2.24 | 0.75-1.25 | |||||
| ASTM A333 Grade 10 | ≤0.20 | 0.10-0.35 | 1.15-1.50 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.015 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.015 | ≤0.50 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.06 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 11 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.35 | ≤0.6 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.50 | 35.0-37.0 | ≤0.50 |
| Grade | Tensile Strength | Yield Point | Elongation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MPa) | (MPa) | Y | X | |
| ASTM A333 Grade 1 | ≥380 | ≥205 | ≥35 | ≥25 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 3 | ≥450 | ≥240 | ≥30 | ≥20 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 4 | ≥415 | ≥240 | ≥30 | ≥16.5 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 6 | ≥415 | ≥240 | ≥30 | ≥16.5 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 7 | ≥450 | ≥240 | ≥30 | ≥22 |
| ASTM A333 Gr. 8 | ≥690 | ≥515 | ≥22 | |
| ASTM A333 Grade 9 | ≥435 | ≥315 | ≥28 | |
| ASTM A333 Grade 10 | ≥550 | ≥450 | ≥22 | |
| ASTM A333 Grade 11 | ≥450 | ≥240 | ≥18 | |
| No. | Order No. | Size description | ||
| O.D./mm | W.T./mm | Legnth/m | ||
| 1 | A333 Gr.6 A333 Gr.6/X42NS | 10~127 | 1~20 | 6~12.0 |
| 42~114.3 | 3.5~6 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 42~114.3 | 6~12 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 114.3~180 | 3.8~8 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 114.3~180 | 8~22 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 68~180 | 10~14 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 69~254 | 14~55 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 140~340 | 6~8 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 140~368 | 8~42 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 318~720 | 14~50 | 4~12.5 | ||
| 2 | A333 Gr.6/X52QS | 42~114.3 | 3.5~12 | 6~12.2 |
| 114.3~180 | 3.8~22 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 68~254 | 10~40 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 140~368 | 6~40 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 318~720 | 14~40 | 4~12.5 | ||
| 140~368 | 6~25 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 318~720 | 14~25 | 4~12.5 | ||
| 3 | 16MnDG | 10~127 | 1~20 | 6~12.0 |
| 42~114.3 | 3.5~12 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 114.3~180 | 3.8~22 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 68~254 | 10~55 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 140~368 | 6~42 | 6~12.2 | ||
| 318~720 | 14~120 | 4~12.5 | ||
| Crade | The lowest temperature for strike test | |
|---|---|---|
| ℉ | ℃ | |
| ASTM A333 Grade 1 | -50 | -45 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 3 | -150 | -100 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 4 | -150 | -100 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 6 | -50 | -45 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 7 | -100 | -75 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 8 | -320 | -195 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 9 | -100 | -75 |
| ASTM A333 Grade 10 | -75 | -60 |
Sunny Steel Supply supplies a full range of ASTM A333 (ASME S/A 333)
Low Temperature Steel Pipe Specifications & Grades
Cold Drawn Seamless Mechanical Tubing (CDS) is a cold drawn 1018/1026 steel tube which offers uniform tolerances, enhanced machinability and increased strength and tolerances compared to hot-rolled products.

Cold drawn steel tube is with hot-rolled steel coil as raw material, and tandem cold rolling pickled to remove oxide scale, its finished rolling hard roll, rolling hard volumes due to the continuous cold deformation caused by cold hardening strength, hardness increased indicators declined tough plastic, stamping performance will deteriorate, which can only be used for simple deformation of the parts.
Rolling hard roll can be used as the raw material of the hot-dip galvanizing plant, hot dip galvanizing line set annealing line. Rolling hard roll weight is generally 6 to 13.5 tons, the coil diameter of 610mm.
Hot-rolled seamless steel pipe production base deformation process can be summarized as three stages: perforation, extension and finishing.
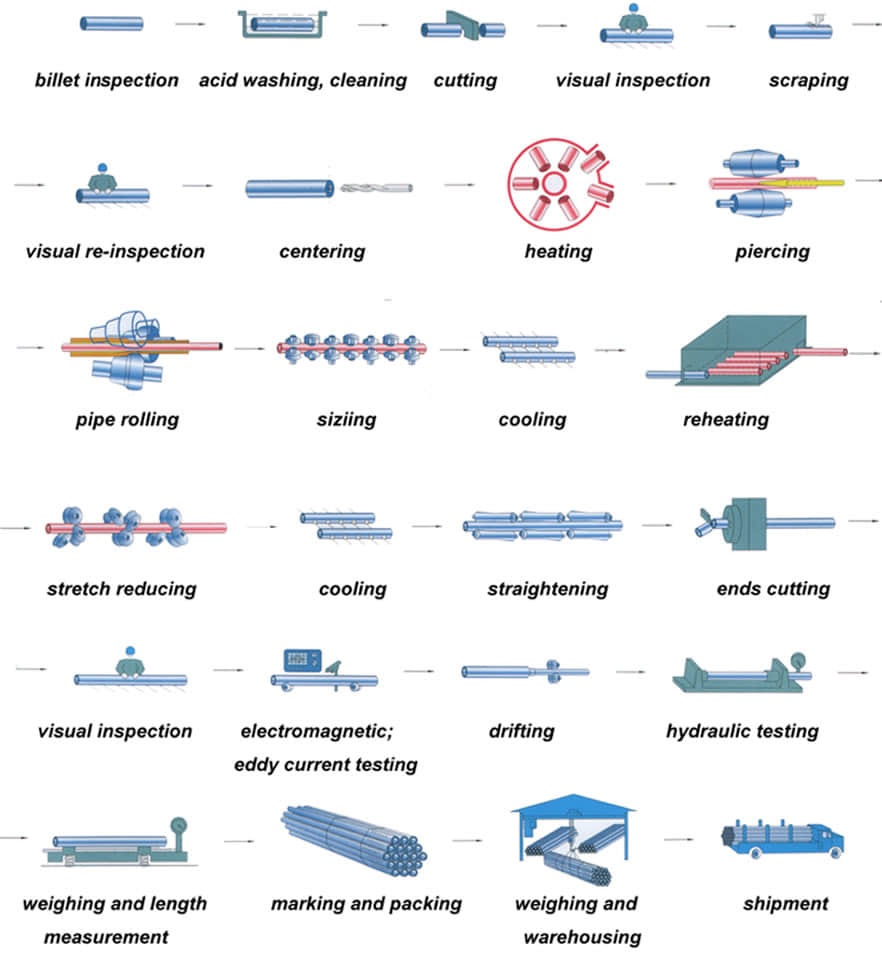
The main purpose of the perforation process is to become a solid round billet piercing hollow shell. Capillary in the specifications, accuracy and surface quality can not meet the requirements of the finished product, further improvements are needed to deform the metal through. The main purpose of the stretching machine is further reduced sectional view (main compression wall) for a larger axial extension, so that the capillary improved dimensional accuracy, surface quality and organizational performance.
After stretching machine rolled steel pipe shortage collectively need further molding mill in order to achieve the requirements of the finished pipe. Rolled steel due to pass in the method widely used in the production of seamless steel tubes.
So far, due to the method pass rolling steel can be divided into two categories: core pension without rolling rolling (hollow body rolling), and with the mandrel. Sizing machines, reducing mill and stretch reducing mill belonging to the hole without mandrel type continuous rolling mills are generally coffin. Its main purpose is to reduce the diameter of the deformation process or sizing get finished steel, the wall thickness of process control, can make thinning, thickening or nearly unchanged.
All the traditional hole-type rolling machine with mandrel belong to extend machine. The main purpose is to reduce the deformation process perforated capillary wall thickness and outer diameter roll passes in the deformation zone and the mandrel posed, for a larger axial extension. At the same time a certain improvement in the organization, performance, accuracy, surface quality.

Before cutting pipe and tubing
No matter the material, measure the diameter of the pipe or tube to be cut to ensure that you use the right-size tube cutter for the job. When determining how to make a straight cut, use a tape measure and a pencil or other writing instrument to mark on the surface where you want to cut. If possible, mark around the circumference of a pipe, especially when cutting with a handsaw. Ensure that a cut is as straight as possible by securing the pipe with a vise, clamp, miter box or even duct tape to keep the length from shifting out of place while cutting.
After cutting pipe and tubing
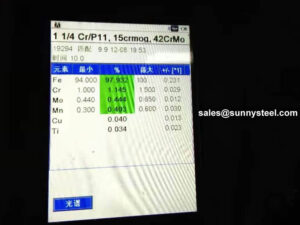
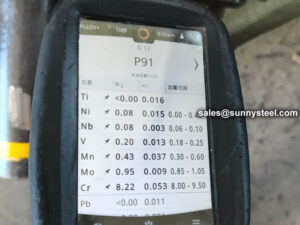
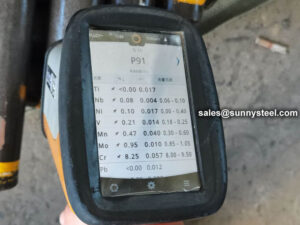
Inspection and test of alloy steel pipe:
Chemical composition inspection, mechanical properties test(tensile strength,yield strength, elongation, flaring, flattening, bending, hardness, impact test), surface and dimension test,no-destructive test, hydrostatic test.









Bare packing/bundle packing/crate packing/wooden protection at the both sides of tubes and suitably protected for sea-worthly delivery or as requested.












 Alloy steel pipes are ideally suitable for chemical, petrochemicals, and other energy-related applications.
Alloy steel pipes are ideally suitable for chemical, petrochemicals, and other energy-related applications.
The alloy steel pipe adopts high quality carbon steel, alloy structural steel and stainless & heat resisting steel as raw material through hot rolling or cold drawn to be made.
Alloy steel can be used in process area where carbon steel has limitation such as
As an important element of steel products, alloy steel pipe can be divided into seamless steel pipe and welded steel pipe according to the manufacturing technique and tube billet shape.
Here you can see the common alloy steel grade that you will come across.
Why the application of alloy steel pipe is wider than others
There are many kinds of materials used for transport in industrial production. Specifically we will have more choices and it is not limited to the use of alloy steel pipe. But even in the face of more choices, many people tend to choose alloy steel pipe. People make their own choices will have their own reasons. This means the alloy steel pipe application has its own advantages. Compared with transmission lines made of other materials, after it meets the basic application requirements, its quantity is lighter. Then in the practical application of alloy steel pipe, it will have more advantages because of this. Besides its physical characteristic advantage, it also has economic advantages. The wide application of alloy steel pipe is with kinds of reasons. So in practical usage, we can exploit the advantages to the full, in this way can we get more profits in these applications of alloy steel pipe.
What requirements should alloy steel pipe application meet
The transportation of kinds of gases or liquids in production needs to rely on alloy steel pipe. This shows that the actual role of alloy steel pipe application is important. High temperature resistant and low temperature resistant is the tolerance of temperature. In the practical application of alloy steel pipe, there will be many materials need to be transported. However their temperatures are not the same. So this can be the basic requirement to alloy steel pipe. It needs more corrosion resistance. Corrosion resistant material is the best material during transporting, because it is corrosion resistant. So it can be used in more occasions. And it is definitely very convenient for users.
The biggest advantages of alloy steel pipe
Can be 100% recycled, environmentally friendly, energy-saving, resource conservation, national strategy, national policy to encourage the expansion of the field of application of high-pressure alloy pipe. Of alloy steel pipe total consumption accounted steel in the proportion is only half of the developed countries, to expand the field of use of the alloy steel pipe to provide a wider space for the development of the industry. The future needs of the average annual growth of China’s high-pressure alloy steel pipe long products up to 10-12%.
Specification, standard and identification of alloy steel pipes
Alloy Steel pipe contains substantial quantities of elements other than carbon such as nickel, chromium, silicon, manganese, tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium and limited amounts of other commonly accepted elements such as manganese, sulfur, silicon, and phosphorous.
Our team of experienced sales specialists proudly partners with gas and chemical processors, power generation plants, oil refineries, and related industries to offer piping components and value-added services.
The biggest advantages of alloy steel pipe can be 100% recycled, environmentally friendly, energy-saving, resource conservation, national strategy, national policy to encourage the expansion of the field of application of high-pressure alloy pipe. Of alloy tube total consumption accounted steel in the proportion is only half of the developed countries, to expand the field of use of the alloy tube to provide a wider space for the development of the industry. According to the Chinese Special Steel Association alloy pipe Branch Expert Group, the future needs of the average annual growth of China’s high-pressure alloy pipe long products up to 10-12%.
Our team of experienced sales specialists proudly partners with gas and chemical processors, power generation plants, oil refineries, and related industries to offer piping components and value-added services.
| Alloying Elements | Effect on the Properties |
|---|---|
| Chromium | Increases Resistance to corrosion and oxidation. Increases hardenability and wear resistance. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Nickel | Increases hardenability. Improves toughness. Increases impact strength at low temperatures. |
| Molybdenum | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Enhances the effects of other alloying elements. Eliminate temper brittleness in steels. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Manganese | Increases hardenability. Combines with sulfur to reduce its adverse effects. |
| Vanadium | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Improves fatigue resistance. |
| Titanium | Strongest carbide former. Added to stainless steel to prevent precipitation of chromium carbide. |
| Silicon | Removes oxygen in steel making. Improves toughness. Increases hardness ability |
| Boron | Increases hardenability. Produces fine grain size. |
| Aluminum | Forms nitride in nitriding steels. Produces fine grain size in casting. Removes oxygen in steel melting. |
| Cobalt | Increases heat and wear resistance. |
| Tungsten | Increases hardness at elevated temperatures. Refines grain size. |
Alloy steels are made by combining carbon steel with one or several alloying elements, such as manganese, silicon, nickel, titanium, copper, chromium and aluminum. These metals are added to produce specific properties that are not found in regular carbon steel. The elements are added in varying proportions (or combinations) making the material take on different aspects such as increased hardness, increased corrosion resistance, increased strength, improved formability (ductility); the weldability can also change.
Norms:
Grade:
Need to inquire about our products? Fill out the form below and our staff will be in touch!
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: The delivery time of customized products is generally 25 35 days, and non customized products are generally shipped within 24 hours after payment.
Q: Do you provide samples? Is it free?
A: If the value of the sample is low, we will provide it for free, but the freight needs to be paid by the customer. But for some high value samples, we need to charge a fee.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: T/T 30% as the deposit,The balance payment is paid in full before shipment
Q: What is the packaging and transportation form?
A: Non steaming wooden box and iron frame packaging. Special packaging is available according to customer needs. The transportation is mainly by sea.
Q: What is your minimum order quantity?
A: There is no minimum order quantity requirement. Customized products are tailor made according to the drawings provided by the customer.