Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199
Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199

Metal pipe expansion joints can withstand the design temperatures, pressures, as well as, provide the capacity necessary to absorb thermal growth of the piping system.
Metal pipe expansion joints can withstand the design temperatures, pressures, as well as, provide the capacity necessary to absorb thermal growth of the piping system.
The thermal movement required can be axial, lateral or angular. In some cases, the pressure thrust of a pipe expansion joint must be restrained by the use of tie rods, hinges or gimbal while allowing the bellows to move through its design deflections.
Sunny Steel offers a wide range of expansion joints, suitable for numerous specific applications.
The Sunny Steel expansion joints portfolio basically consists of three main series:
The heart of all expansion joints is the metal bellows. Thanks to modern design and manufacturing facilities, all BOA expansion joints offer the following advantages:
Storage:
Handling:
Do not lift with ropes or bars through the bolt holes. If lifting through the bore, use padding or a saddle to distribute the weight. Do not let expansion joints sit vertically on the edges of the flanges for any period of time. Do not lift on the shipping restraints.
Make sure the expansion joint rating for temperature, pressure, movements, and selection of materials match the system requirements. Contact the manufacturer if the system requirements exceed those of the expansion joint selected.
Alignment
Expansion joints are not designed to make up for piping misalignment errors. Check with the manufacturer if piping misalignment is present.
Anchoring
The main function of expansion joints is to compensate for axial pipe thermal expansion. Metal expansion joints must have the protection of adequate anchoring against the internal and thrust pressures of the media to prevent damage. Anchoring must be installed as close to the down stream end of the expansion joint as possible, with the originating equipment serving as the opposite anchor. Anchors must prevent pipe movement in any direction. Hangers or pipe pedestals cannot be considered to be anchors as they offer no restriction against side or end motion.
When designing an anchor for a metal expansion joint, consult the internal thrust force table from the appropriate expansion joint catalogue. The weight of piping, valves, and media, as well as the resistance of the piping to deflection, must be included as part of the design weight and strength of an anchor.
Anchors are required whenever a piping system changes direction. Expansion joints should be located as close as possible to anchor points. For additional expansion joint protection, it is recommended that control rods be installed on the expansion joint to prevent excessive movements from occurring due to pressure thrust of the line.
Guides:
Expansion joints must be properly guided and anchored in accordance with EJMA standards.
Pipe Support:
Piping must be supported so expansion joints do not carry any pipe weight.
Mating Flanges:
Install the expansion joint flange against the mating pipe flanges and install bolts so that the bolt head is against the expansion joint flange. Bolts should be installed from the bellows side (so that the bolt heads are adjacent to the bellows) to insure that the bolts do not interfere with the bellows during periods of compression. Flange-to-flange dimensions of the expansion joint must match the required opening.
Make sure mating flanges are clean and are matched to the type supplied with the expansion joint. Gaskets of appropriate material, size and temperature ratings must be used in all flange-to-flange type installations.
Bolt Torque:
Tighten bolts in stages by alternating around the flange. Never tighten an expansion joint to the point that there is
metal-to-metal contact between the expansion joint flange and the mating flange.
Shipping Restraints:
The expansion and compression movements are preset at the factory. The shipping restraints protect the expansion joint in its neutral position prior to installation. Remove the shipping restraints after installation and before hydro-testing the system.
Compensator reliability is by the design, manufacture, installation and operation and management and other aspects of the composition. Reliability should also be considered from these aspects.
Material Selection For the selection of corrugated pipe for heating pipe network, in addition to considering the working medium, working temperature and the external environment, the possibility of stress corrosion should also be considered, the impact of water treatment agent and pipe cleaning agent on the material, etc.,
Based on this, the corrugated pipe material is welded and formed, and the cost performance of the material is optimized. The economical and practical corrugated pipe material is selected.
Under normal circumstances, the use of corrugated pipe material should meet the following conditions:
For the laying of the heat pipe network, when the compensator is located in the lower pipelines, rain or accidental sewage will soak corrugated pipe, should consider the use of more corrosion-resistant materials, such as iron-nickel alloy, high-nickel alloy. Due to the high price of such materials, it may be advisable to add a corrosion-resistant alloy only to the surface in contact with the corrosive medium when making the bellows.
In a piping system a Expansion joints alternately known as Bellows are like sealed springs. Sealed because it is required to contain the fluid pressure which is flowing through it and spring because it is required to respond to the movement of the connected piping without offering appreciable stiffness to the piping system.
An expansion joint/bellow element employed in a piping system is an assembly of generally more than one convolute in series. The convolutes are designed strong enough to withstand the internal pressure of the system, at the same time the typical contour of the convolute assembly allow sit to flex under thermal movement of the connected piping. As a result of this extreme flexibility the expansion joint / bellow as such is highly incapable of absorbing any longitudinal loads by its own,thereby requiring external attachments to transfer these longitudinal loads to its connected piping for maintaining the overall stability of the piping system under question.
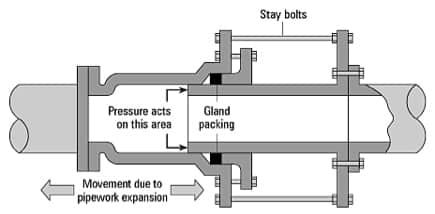
However should site conditions demand a unique solution then end connections can be adapted to most applications.
The terms can be confusing since there is no universally accepted meaning. We usually use the following definitions, but the terms “bellows” and “expansion joint” are generally considered interchangeable:
Pipe expansion joints are also known as compensators, as they ‘compensate’ for the thermal movement.
Pipe expansion joints are necessary in systems that convey high temperature commodities such as steam or exhaust gases, or to absorb movement and vibration. A typical type of expansion joint for pipe systems is a bellows which can be manufactured from metal (most commonly stainless steel), plastic (such as PTFE), or an elastomer such as rubber.
A bellows is made up of a series of one or more convolutions, with the shape of the convolution designed to withstand the internal pressures of the pipe, but flexible enough to accept the axial, lateral, and/or angular deflections. Expansion joints are also designed for other criteria, such as noise absorption, anti-vibration, earthquake movement, and building settlement.
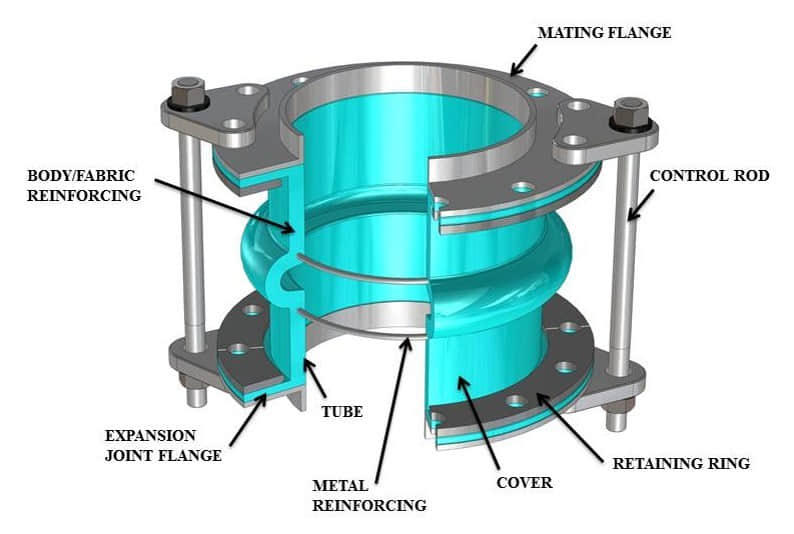
Tube – A protective, leak proof lining made of synthetic or natural rubber. The tubes primary function is to eliminate the possibility of materials being handled penetrating the carcass.
Carcass – The carcass or body of the expansion joint consists of fabric, and when necessary metal.
Cover – The exterior surface of the joint.
Fabric Reinforcement – The carcass fabric reinforcement is the flexibility and supporting member between the tube and cover.
Metal Reinforcement – Wire or solid steel rings imbedded in the carcass, often used for strengthening.
Retaining Ring – Used to compress the expansion joint flange to the mating flange to create a seal. Also called clamp bars or backing bars. Applies to most all expansion joints.
Mating Flange – Used to connect the pipe joint to the pipe in which it is being installed.
Control Rod – Used to limit the axial movements during operation, and prevent the joint from exceeding its movement capabilities. The rods attach the mating flange and expansion joint. Typically used on piping joints, but can be installed on most any joint when required.
Expansion joints are an assembly designed to safely absorb sound, expansion, con traction and vibration to ensure expansion jointsthat the application stays in fully working order.
When we apply this technique to pipe systems, we brand the term ‘pipe expansion joint’ or ‘bellows’.
These pieces of equipment are used in pipe work where movement, thermal expansion and much more could cause problems. The pipe expansion joints are made up from one or more convolutions, which are designed to move or expand to relieve the stress from the solid pipe. The amount of movement or expansion within the application will determine the number and shape of convolutions required. Expansion joints can be manufactured from a range of different materials, from stainless steel and PTFE, to rubber.
Pipe expansion joints are also designed for other criteria, such as noise absorption, anti vibration, earthquake movement and building settlement. Metal expansion joints have to be designed according to rules. Pipe expansion joints are used in a number of industries, including; oil, petrochemical and paper industries.
Pipe expansion joints are often manufactured to withstand temperatures from minus 300°F, up to 4000°F, as well as being able to resist at full vacuum or 2000 psig. Expansion joints can be manufactured from a range of different materials aforementioned. Before the introduction of pipe expansion joints, engineers were battling with the task of combating problems regarding thermal expansion, corrosion and abrasive factors that took effect on the functionality of various applications. Fabric joints can be used in a number of applications for turbines and pipelines, which can defend against resistance, heat and a range of other environmental factors.
Pipe expansion joints are crucial components in the pipe technology sector, which serve a huge number of industries. They are used to counterbalance length changes that generally occur in pipelines from temperature changes and can also absorb vibrations. It is a cost effective solution to increase the life span, reliability and costs of many applications through equipment and process management.
Accessories are added to an expansion joint installation to meet specific customer, application or code requirements. Some are used to control movement, others to protect the bellows in the event of pressure thrust, and still others to defend against corrosion caused by media inside or from the environment outside the bellows.
Internal sleeves
Anchor base
Divide piping into two separate segments insuring proper movement of each bellows in double type expansion joint.
External cover
Purge aeration connections
Used in conjunction with internal sleeve to:
Tie rods
Oversized bellows
Liners
Internal liners can be used to either protect the metallic bellows from erosion or reduce turbulence across the bellows. They must be used when purge connectors are included in the design. In order to provide enough clearance in the liner design, appropriate lateral and angular movements must be specified by the designer. When designing an expansion joint with combination ends, flow direction must be specified as well.
Covers
External covers should be used to protect the internal bellows from being damaged. They also serve a purpose as insulation of the bellows. Covers can either be designed as removable or permanent accessories.
Particulate barriers/purge connectors
In systems that have a media with significant particulate content (i.e. flash or catalyst), a barrier of ceramic fiber can be utilized to prevent corrosion and restricted bellows flexibility resulting from the accumulation of the particulate. Purge connectors may also be utilized to perform this same function. Internal liners must also be included in the design if the expansion joint includes purge connectors or particulate barriers.
Limit rods
Limit rods may be used in an expansion joint design to limit the axial compression or expansion. They allow the expansion joint to move over a range according to where the nut stops are placed along the rods. Limit rods are used to prevent bellows over-extension while restraining the full pressure thrust of the system.
Pipe expansion joints are necessary in systems that convey high temperature commodities such as steam or exhaust gases, or to absorb movement and vibration. An expansion joint is a useful component in an infinite number of applications.
A bellows is made up of a series of one or more convolutions, with the shape of the convolution designed to withstand the internal pressures of the pipe, but flexible enough to accept the axial, lateral, and/or angular deflections.
Expansion joints are also designed for other criteria, such as noise absorption, anti-vibration, earthquake movement, and building settlement.
Engineers and pipe designers routinely incorporate expansion joints into their pipe systems, as expansion joints add flexibility in to the design and reduce costs through removing the complexity of fix points, guides and reduces the overall space requirements for the pipe system.
Further, expansion joints are more effective than alternatives such as pipe bends and pipe loops due to their greater ability to conserve space, their economic efficiency and better performance in absorbing larger movements.
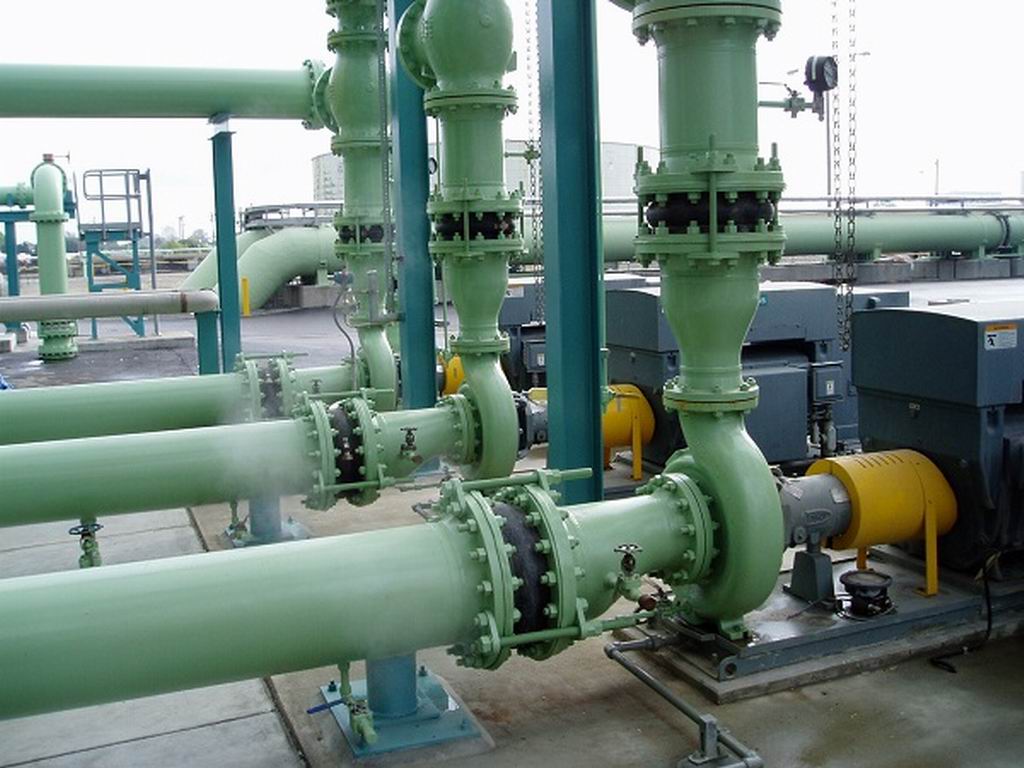

An expansion joint is a useful component in an infinite number of applications. Metal expansion joint assemblies are commonly used for all kinds of industries and applications including:
Expansion joints are often installed near boilers, heat exchangers, pumps, turbines, condensers, engines and in long pipe systems or pipe ducts.
Expansion joints come in a wide variety of designs. Some of them are standard and some are customised as per client requirements.
Although their design may vary significantly, all expansion joints are nevertheless composed from some of the following components, all with one or more specific functionalities: bellows, welding ends, flanges, hinges, tie-rods, spherical washers, wire mesh, insulation, inner sleeve, external cover, elbow and/or ring reinforcement/equalizing rings.
In general, there are fabric, metallic, and rubber expansion joints.
In a piping system a Expansion joints alternately known as Bellows are like sealed springs. Sealed because it is required to contain the fluid pressure which is flowing through it and spring because it is required to respond to the movement of the connected piping without offering appreciable stiffness to the piping system.
The Bellows are generally employed in a piping system in one of the following situations:
An expansion joint or movement joint is an assembly designed to safely absorb the heat-induced expansion and contraction of construction materials, to absorb vibration, to hold parts together, or to allow movement due to ground settlement or earthquakes.
They are commonly found between sections of buildings, bridges, sidewalks, railway tracks, piping systems, ships, and other structures.
Expansion joints – sometimes called expansion bellows, flexible joints or Expansion joint – are devices that comprise of a flexible element known as the bellows membrane that is fitted to end connections that are best suited to the pipework they are to be installed in.
Most bellows membranes are manufactured from stainless steel and are made up of a series of convolutions manufactured to withstand the pressure of the system but also must be suitable to accept the movements for which they are designed. The bellows membrane comprises of a series of convolutions designed to withstand the internal pressures of the system, but at the same time flexible enough to accept axial, lateral and angular deflections.
The joint needs to be a highly resistant nature so it’s necessary to make sure that it’s far thicker than you’d expect. In turn, this slows down any effects of potential corrosion as although it may be affected by the elements over time, it will still retain its density.
Expansion joints are required in large ducted air systems to allow fixed pieces of piping to be largely free of stress as thermal expansion occurs.
Bends in elbows also can accommodate this.
Expansion joints also isolate pieces of equipment such as fans from the rigid ductwork thereby reducing vibration to the ductwork as well as allowing the fan to “grow” as it comes up to the operating air system temperature without putting stress on the fan or the fixed portions of ductwork.
An expansion joint is designed to allow deflection in the axial(compression) or laterally (shear) or angular (bending) deflections. Expansion joints can be non-metallic or metallic (often called bellows type). Non-metallic can be a single ply of rubberized material or a composite made of multiple layers of heat and erosion resistant flexible material.
Typical layers are: outer cover to act a gas seal, a corrosion resistant material such as Teflon, a layer of fiberglass to act as an insulator and to add durability, several layers of insulation to ensure that the heat transfer from the flue gas is reduced to the required temperature and an inside layer.
A bellows is made up of a series of one or more convolutions of metal to allow the axial, lateral or angular deflection required.
Expansion joints are used in all kinds of different sectors and in a huge range of different industrial contexts.
Specific industries that use expansion joints include the Energy sector such as nuclear power plants and district heating schemes.
Essentially, wherever there is a need to control pipework movement expansion joints are required. They are used in factories and power plants wherever thermal expansion needs to be controlled, such as pipelines that connect with condensers or power turbines. They are used in oil and fuel gas applications.
The Petrochemical industry on oil refineries, pumping stations and oil rigs.
Civil engineering, waste management, sewage treatment, recycling, water treatment, aerospace, aviation, defence, the automotive industry, agriculture, mining, metals manufacturing, food and dairy manufacturing and packaging, and so on.





Courier company transport, air freight and sea transport. It depends on your actual order details and quantity.
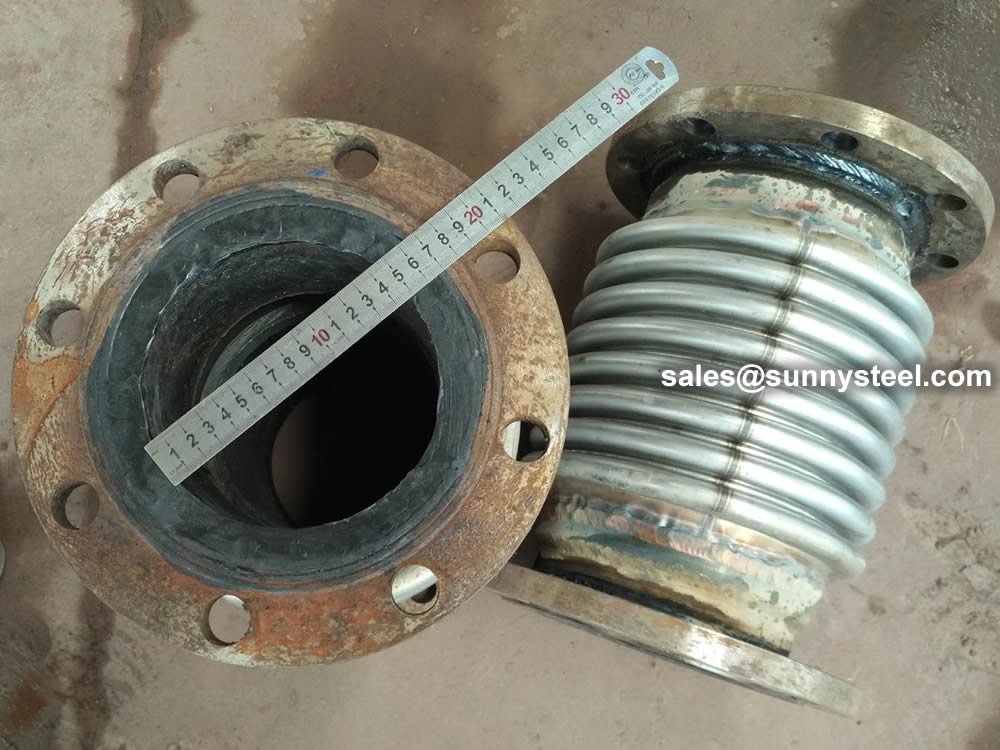


Size measurement of expansion joints
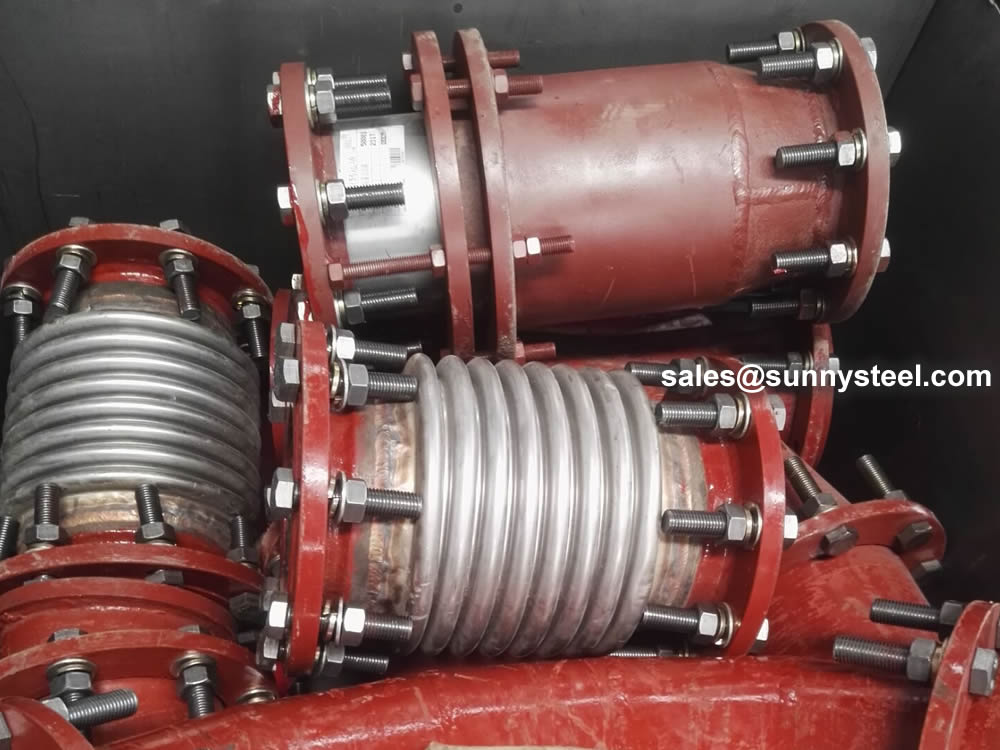

Packing ceramic lined pipe expansion joints
Need to inquire about our products? Fill out the form below and our staff will be in touch!
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: The delivery time of customized products is generally 25 35 days, and non customized products are generally shipped within 24 hours after payment.
Q: Do you provide samples? Is it free?
A: If the value of the sample is low, we will provide it for free, but the freight needs to be paid by the customer. But for some high value samples, we need to charge a fee.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: T/T 30% as the deposit,The balance payment is paid in full before shipment
Q: What is the packaging and transportation form?
A: Non steaming wooden box and iron frame packaging. Special packaging is available according to customer needs. The transportation is mainly by sea.
Q: What is your minimum order quantity?
A: There is no minimum order quantity requirement. Customized products are tailor made according to the drawings provided by the customer.